No matter what the industry or product, there is only one thing that limits how ParaGlass and ParaTank can be used – imagination. Here are some examples of how Parabeam products are currently being used.
1 Nose cone / 2 Endcap and side panels / 3 Ceiling panel interior (core) / 4 Floor panel (lightweight core) and heated-floor system / 5 Air-conditioning condenser / 6 Door (secondary core) and door panel / 7 Section divider and bulkhead / 8 Toilet cabin
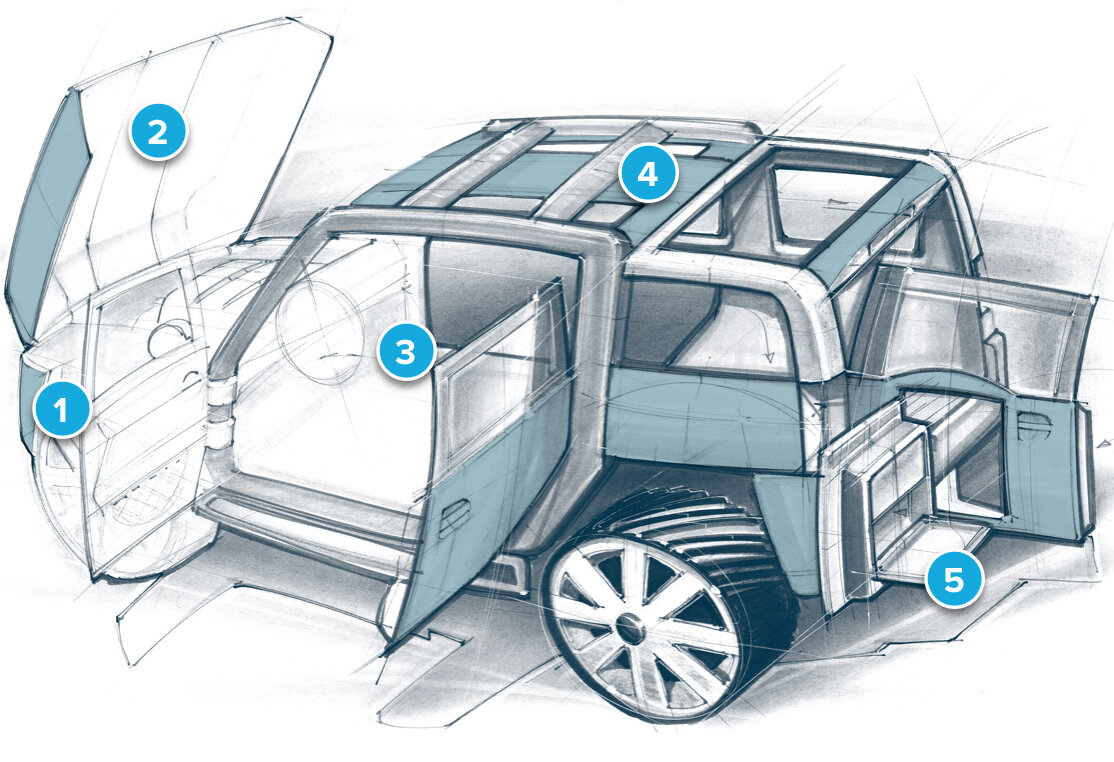
1 Spoiler and air deflector / 2 Hood (core material) / 3 Seat (flexible core material) / 4 Complete roof structure / 5 Storage boxes
Ground Transportation
ParaGlass proves its versatility as a sustainable solution in all forms of ground transportation. Its favorable weight-to-strength ratio and high FST (fire, smoke, toxicity) properties make it easy for companies to meet carbon footprint requirements in mass transportation and individual vehicles. This makes it extremely valuable when manufacturing parts for electric vehicles.
Resistant to decay, fungi and algae, ParaGlass is applied as the primary core for floor heating in trains and busses. In tropical areas, it is used in condenser systems for air-conditioned metro and train carriages. More economical and lightweight as a secondary core than honeycomb, it is often used as a sound and temperature insulator in rail cars. It can also be used as cladding when refurbishing trains.
Marine
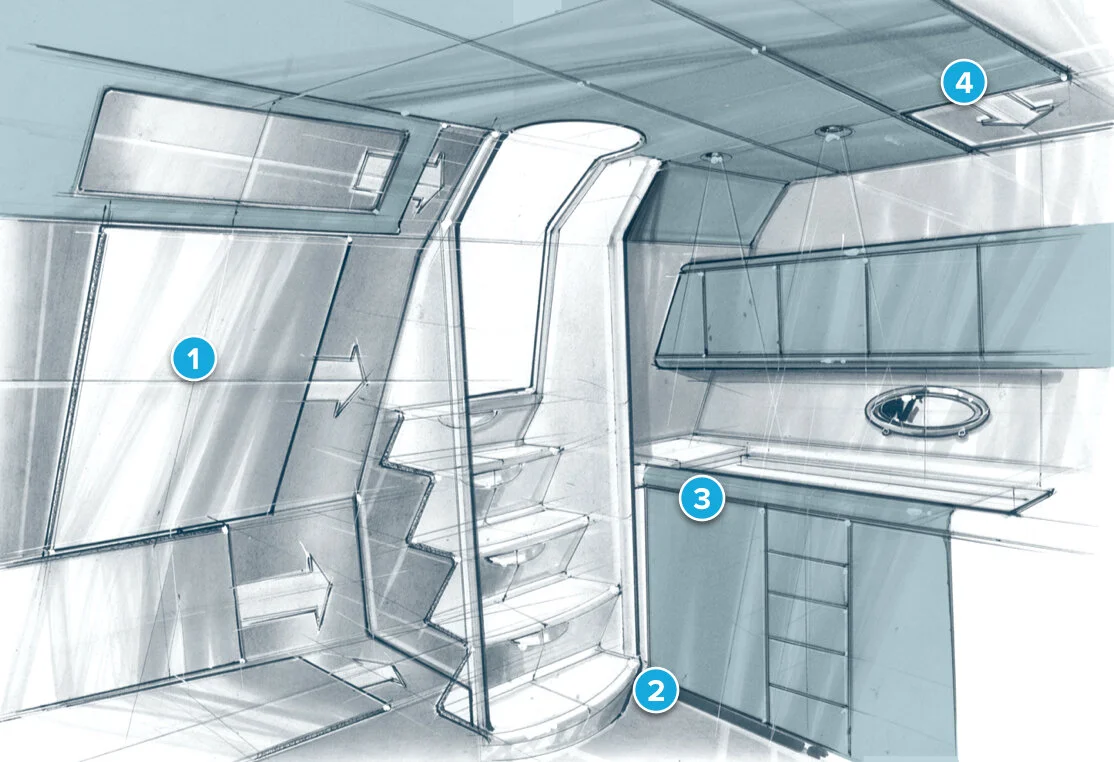
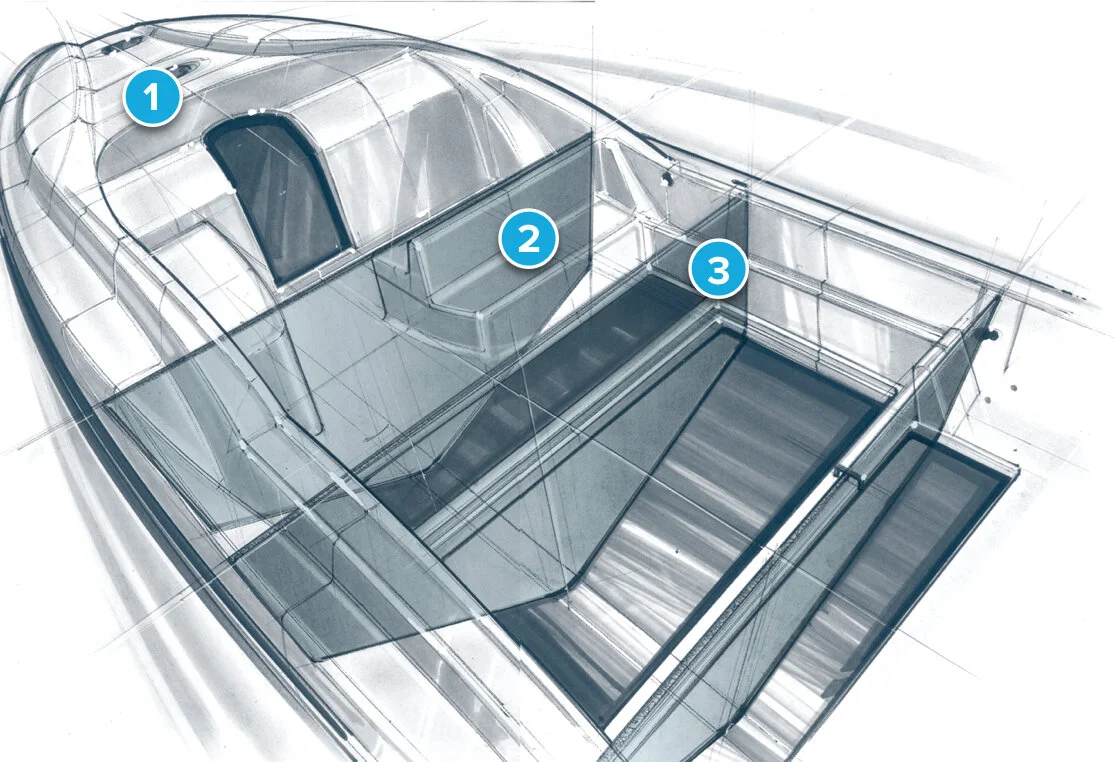
Resistant to humidity and corrosion, ParaGlass offers many advantages in marine vessels. It is highly drapeable, and bonds well with other construction materials, such as wood, foam, steel and aluminum. Its high insulation properties adds value in any type or size of watercraft.
ParaGlass is stronger the plywood, less costly than teakwood, and lighter and easier to apply than honeycomb. With a one-step lamination process that saves labor time and cost, it is commonly used in flybridges, swimming platforms and engine covers, as well as areas shown here.
1 Hatches / 2 Flooring / 3 Cabinets / 4 Ceiling panels
1 Decks / 2 Seating / 3 Interior panels
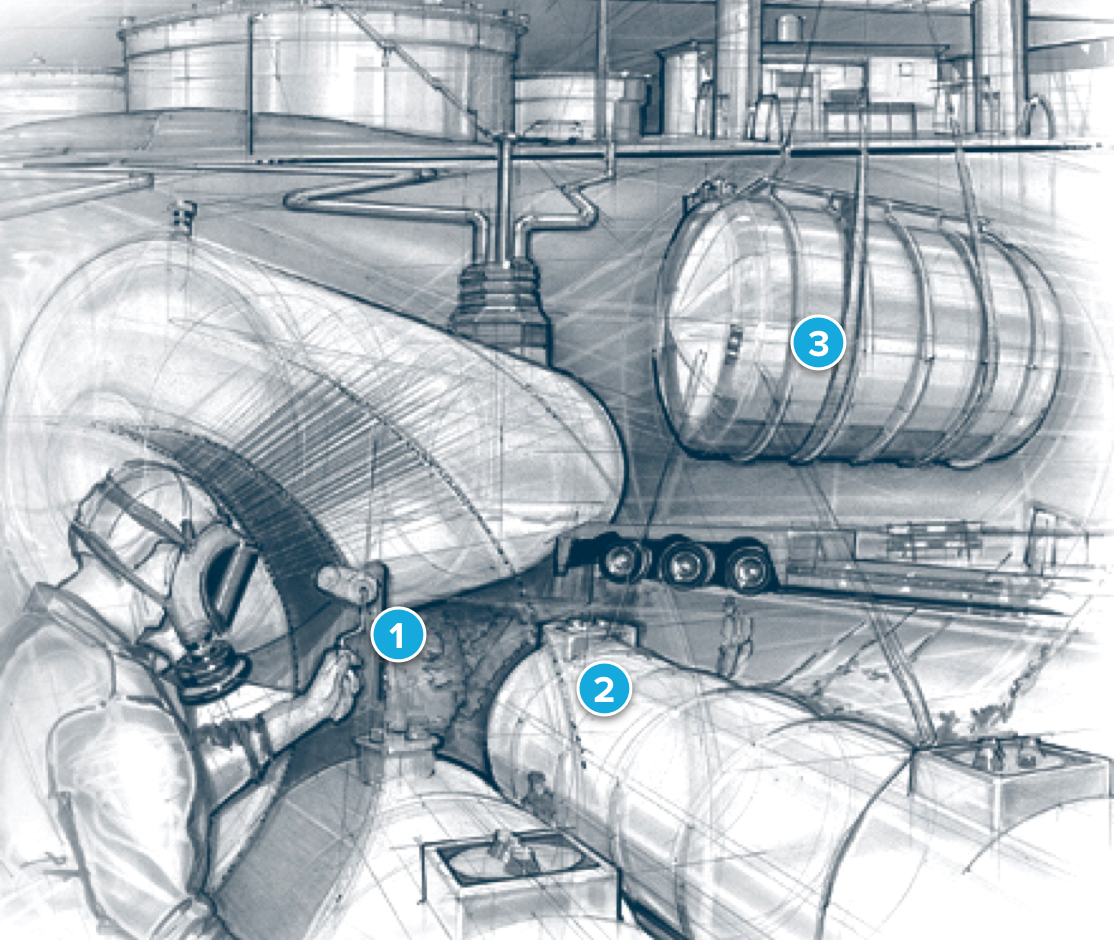
1 Aboveground tank cover / 2 Laminate for structural strength / 3 Interstice for bottom leak detection
1 Tank lining creates a corrosion-resistant tank within a tank / 2 The E‑glass fabric provides an interstice for continuous leak detection / 3 The 3D‑glass fabric bonds tank walls for increased structural strength
Tanks & Tank Linings
ParaTank is commonly used in both composite and steel tanks. In fiberglass tanks, the 3D e‑glass material bonds the walls of double-wall tanks and containment sumps. This creates an interstitial space that allows for continuous leak monitoring.
In both fiberglass and steel single-wall tanks, ParaTank creates a lining inside the tank that virtually turns the tank into a double-wall tank. This tank lining turns a steel tank into a corrosion-resistant tank. It is easy to install and can be done with the tank in situ.

1 Cockpit liner / 2 Section divider / 3 Tray tables (core) / 4 Engine cowl
Aerospace
In any type and size of aircraft, ParaGlass is increasingly used because of its advantages over other core materials such as honeycomb, fiberglass or Nomex®. Though lightweight, it provides constant compressive strength and balance, and has extremely high FST (fire, smoke, toxicity) properties when combined with fire-retardant resins.
Combining E‑glass with aramid also increases the strength of the sandwich material. The drapeability of ParaGlass makes it adaptable to countless placements, from bulkheads and cockpits to interior ceilings and walls. In smaller planes, it is also used for propellers.
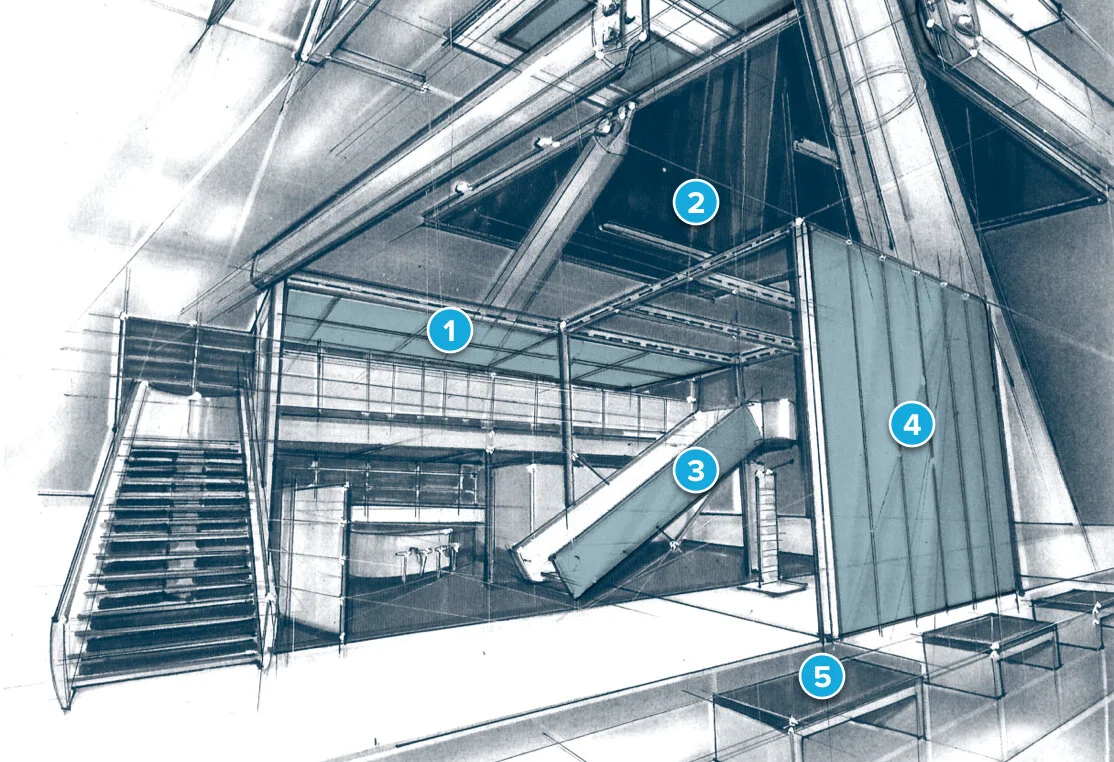
1 Ceiling panels / 2 See-through daylight panels / 3 Lightweight panel replacement / 4 Exterior walls / 5 Furniture
Building & Construction
When rating common construction materials, 3D E‑glass fabrics test highest in measures such as energy absorption and high crush-force efficiency. This gives ParaGlass an edge over options such as metals, woods and nonwoven plastics.
ParaGlass is up to 50% lighter than standard fire-retardant fiberglass, and up to 50% less costly to ship than metal sheets. This strong, thin material can provide a lower material cost than alternate materials. In buildings, domes and any architectural design, woven E‑glass fabric makes complex shapes easy to construct, often eliminating complicated assembly and welding. An example of its adaptability is that ParaGlass can be applied as a backing to reinforce flat marble facades and curved marble cladding.
Tools & Moulding
The material thickness and drapeability of ParaGlass make it easier to achieve desired shapes when making tools and moulds. Using e‑glass sandwich fabric can save up to 20% in overall costs, with reduced labor, lower energy consumption and increased tool life.
ParaGlass is superior to traditional fiberglass in numerous ways. Set-up time is decreased by up to 50%. Using hot water instead of hot air makes it a more precise and energy-efficient method of curing. Resistance to temperature extremes, it is highly adaptable for use and storage in any conditions.
Energy
The inherent sustainability properties of ParaGlass – corrosion-resistance, favorable weight-to-strength ratio and adaptability – make it an ideal material for manufacturing products for the energy industry. In many ways, it is preferable to other commonly used materials, such as steel, aluminium and solid-glass laminates.
In wind turbines, ParaGlass has many advantages over steel. For instance, the E‑glass woven fabric reduces both the weight and cost of turbine towers and nacelle covers without compromising on strength. When used in heat exchangers and as a reinforcement in solar panels, the open space of the sandwich material has the added benefit of cooling.

Application illustrations by Frans Hegge